We develop various miniaturised electrochemical sensors for both short biologically active molecules and proteins for various fields of applications such as food quality control, medical diagnostics, water quality. The main tasks are design of the sensing part and selection of materials to enhance response signal as well as lower limit of detection. Some sensors are single use, others are stable for longer time. Carbon nanomaterials and conducting polymers composed from natural monomers, in particular B group vitamins and amino acids, are used in sensor development. Often selectivity is assured employing enzymes or antibodies.
We developed sensors for such analytes: glutamate, cholesterol, vitamin C, hypoxanthine, dopamine and uric acid. We also have experience with electrochemical trace determination of some heavy metals in drinking or waste water.
Article example: L. Laurinavičius, A. Radzevič, I. Ignatjev, G. Niaura, K. Vitkutė, Titas Širšinaitis, R. Trusovas, R. Pauliukaite, Investigation of electrochemical polymerisation of L-lysine and application for immobilisation of functionalised graphene as platform for electrochemical sensing, Electrochimica Acta 299 (2019) 936e945, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2019.01.079
Some examples of the developed electrodes
Our examples:
![]()
Laser structured 1 μm stripe (right hand side) graphene-chitosan electrode modified with polyriboflavin on glass with golden contacts, for glutamate detection. Chip size 5×7 mm .
![]()
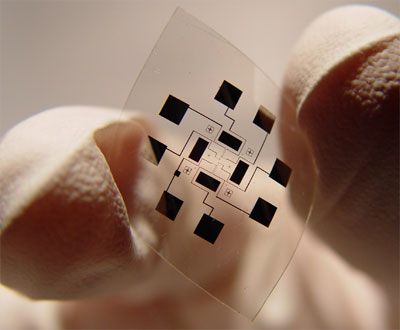
Interdigitated Au electrode prepared by soft nanolithography for further modification and electroanalysis of cell metabolites. Chip size 10×10 mm .